- Which statement describes a typical security policy for a DMZ firewall configuration?
- Traffic that originates from the inside interface is generally blocked entirely or very selectively permitted to the outside interface.
- Traffic that originates from the DMZ interface is selectively permitted to the outside interface.*
- Traffic that originates from the outside interface is permitted to traverse the firewall to the inside interface with few or no restrictions.
- Return traffic from the inside that is associated with traffic originating from the outside is permitted to traverse from the inside interface to the outside interface.
- Return traffic from the outside that is associated with traffic originating from the inside is permitted to traverse from the outside interface to the DMZ interface.
With a three interface firewall design that has internal, external, and DMZ connections, typical configurations include the following:
Traffic originating from DMZ destined for the internal network is normally blocked.
Traffic originating from the DMZ destined for external networks is typically permitted based on what services are being used in the DMZ.
Traffic originating from the internal network destined from the DMZ is normally inspected and allowed to return.
Traffic originating from external networks (the public network) is typically allowed in the DMZ only for specific services.
- Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the function of the ACEs?

- These ACEs allow for IPv6 neighbor discovery traffic.*
- These ACEs automatically appear at the end of every IPv6 ACL to allow IPv6 routing to occur.
- These are optional ACEs that can be added to the end of an IPv6 ACL to allow ICMP messages that are defined in object groups named nd-na and nd-ns.
- These ACEs must be manually added to the end of every IPv6 ACL to allow IPv6 routing to occur.
The ICMP protocol is used for neighbor discovery. The two permit statements allow neighbor advertisement and neighbor solicitation messages between IPv6 devices.
- When an inbound Internet-traffic ACL is being implemented, what should be included to prevent the spoofing of internal networks?
- ACEs to prevent traffic from private address spaces*
- ACEs to prevent broadcast address traffic
- ACEs to prevent ICMP traffic
- ACEs to prevent HTTP traffic
- ACEs to prevent SNMP traffic
Common ACEs to assist with antispoofing include blocking packets that have a source address in the 127.0.0.0/8 range, any private address, or any multicast addresses. Furthermore, the administrator should not allow any outbound packets with a source address other than a valid address that is used in the internal networks of the organization.
- In addition to the criteria used by extended ACLs, what conditions are used by a classic firewall to filter traffic?
- TCP/UDP source and destination port numbers
- TCP/IP protocol numbers
- IP source and destination addresses
- application layer protocol session information*
The classic firewall provides stateful inspection including protocols that require multiple channels for communication such as FTP and H.323. Protocol numbers, port numbers, and source and destination IP addresses are all standard filters for extended ACLs.
- A router has been configured as a classic firewall and an inbound ACL applied to the external interface. Which action does the router take after inbound-to-outbound traffic is inspected and a new entry is created in the state table?
- When traffic returns from its destination, it is reinspected, and a new entry is added to the state table.
- The internal interface ACL is reconfigured to allow the host IP address access to the Internet.
- The entry remains in the state table after the session is terminated so that it can be reused by the host.
- A dynamic ACL entry is added to the external interface in the inbound direction.*
The traffic flow from the internal network to the public network is commonly inspected. The traffic flows cause dynamic entries to be added to the external interface for inbound traffic so that traffic that originates from the internal network going to the public network is allowed to return to the internal source.
- Refer to the exhibit. If a hacker on the outside network sends an IP packet with source address 172.30.1.50, destination address 10.0.0.3, source port 23, and destination port 2447, what does the Cisco IOS firewall do with the packet?
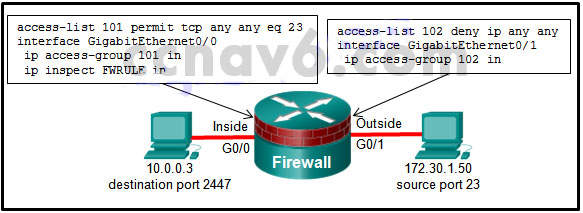
- The initial packet is dropped, but subsequent packets are forwarded.
- The packet is forwarded, and an alert is generated.
- The packet is forwarded, and no alert is generated.
- The packet is dropped.*
This ACL is denying all TCP/IP traffic coming into the outside interface. Because the source address matches the any parameter and because the access list line is filtering based on denying access (deny), the packet is dropped.
- What is one benefit of using a stateful firewall instead of a proxy server?
- ability to perform user authentication
- better performance*
- ability to perform packet filtering
- prevention of Layer 7 attacks
A stateful firewall performs better than a proxy server. A stateful firewall cannot authenticate users or prevent Layer 7 attacks. Both a stateful firewall and a proxy server can filter packets.
- What is one limitation of a stateful firewall?
- weak user authentication
- cannot filter unnecessary traffic
- not as effective with UDP- or ICMP-based traffic*
- poor log information
Limitations of stateful firewalls include the following:
Stateful firewalls cannot prevent application layer attacks.
Protocols such as UDP and ICMP are not stateful and do not generate information needed for a state table.
An entire range of ports must sometimes be opened in order to support specific applications that open multiple ports.
Stateful firewalls lack user authentication.
- To facilitate the troubleshooting process, which inbound ICMP message should be permitted on an outside interface?
- echo request
- time-stamp request
- echo reply*
- time-stamp reply
- router advertisement
By allowing the ICMP echo reply message inbound to the organization, internal users are allowed to ping external addresses (and the reply message allowed to return).
- Which command is used to activate an IPv6 ACL named ENG_ACL on an interface so that the router filters traffic prior to accessing the routing table?
- ipv6 access-class ENG_ACL in
- ipv6 traffic-filter ENG_ACL out
- ipv6 traffic-filter ENG_ACL in*
- ipv6 access-class ENG_ACL out
For the purpose of applying an access list to a particular interface, the ipv6 traffic-filter IPv6 command is equivalent to the access-group IPv4 command. The direction in which the traffic is examined (in or out) is also required.
- If the provided ACEs are in the same ACL, which ACE should be listed first in the ACL according to best practice?
- permit udp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 host 172.16.1.5 eq snmptrap*
- deny udp any host 172.16.1.5 eq snmptrap
- deny tcp any any eq telnet
- permit ip any any
- permit udp any any range 10000 20000
- permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.3.255 any established
A best practice for configuring an extended ACL is to ensure that the most specific ACE is placed higher in the ACL. Consider the two permit UDP statements. If both of these were in an ACL, the SNMP ACE is more specific than the UDP statement that permits a range of 10,001 UDP port numbers. The SNMP ACE would be entered before the other UDP ACE. The ACEs from most specific to least specific are as follows:
permit udp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 host 172.16.1.5 eq snmptrap
deny udp any host 172.16.1.5 eq snmptrap
permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.3.255 any established
deny tcp any any eq telnet
permit udp any any range 10000 20000
permit ip any any
- Which security tool monitors network traffic as it flows into and out of the organization and determines whether packets belong to an existing connection or are from an unauthorized source?
- web security appliance
- intrusion protection system
- application proxy
- stateful firewall*
A stateful firewall filters packets based on state information maintained in a state table. Because it uses state information, the stateful firewall can analyze traffic at OSI Layers 4 and 5.
- A company is deploying a new network design in which the border router has three interfaces. Interface Serial0/0/0 connects to the ISP, GigabitEthernet0/0 connects to the DMZ, and GigabitEthernet/01 connects to the internal private network. Which type of traffic would receive the least amount of inspection (have the most freedom of travel)?
- traffic that is going from the private network to the DMZ*
- traffic that is returning from the DMZ after originating from the private network
- traffic that originates from the public network and that is destined for the DMZ
- traffic that is returning from the public network after originating from the private network
Most traffic within an organization originates from a private IP address. The amount of inspection done to that traffic depends on its destination or whether traffic that is going to that private IP address originated the connection. The demilitarized zone typically holds servers. Traffic that is destined to those servers is filtered based on what services are being provided by the server (HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, etc.).
- Refer to the exhibit. The ACL statement is the only one explicitly configured on the router. Based on this information, which two conclusions can be drawn regarding remote access network connections? (Choose two.)

- SSH connections from the 192.168.2.0/24 network to the 192.168.1.0/24 network are allowed.
- Telnet connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are allowed.
- Telnet connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are blocked.*
- SSH connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are allowed.*
- SSH connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are blocked.
- Telnet connections from the 192.168.2.0/24 network to the 192.168.1.0/24 network are allowed.
The extended access list in the exhibit is permitting SSH (TCP port 22) traffic that is sourced from the 192.168.1.0/24 network and traveling to the 192.168.2.0/24 network. The packets meeting this criteria are logged to the local logging buffer (the default), a syslog server, or both depending on how the router is configured for syslog settings. All other traffic is denied because of the implicit deny at the end of every ACL.
- Consider the following access list.
access list.access-list 100 permit ip host 192.168.10.1 any
access-list 100 deny icmp 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 any echo
access-list 100 permit ip any any
Which two actions are taken if the access list is placed inbound on a router Gigabit Ethernet port that has the IP address 192.168.10.254 assigned? (Choose two.)
- Only the network device assigned the IP address 192.168.10.1 is allowed to access the router.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network are not allowed to reply to any ping requests.
- Only Layer 3 connections are allowed to be made from the router to any other network device.
- Devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network are not allowed to ping other devices on the 192.168.11.0 network.*
- A Telnet or SSH session is allowed from any device on the 192.168.10.0 into the router with this access list assigned.*
The first ACE allows the 192.168.10.1 device to do any TCP/IP-based transactions with any other destination. The second ACE stops devices on the 192.168.10.0/24 network from issuing any pings to any other location. Everything else is permitted by the third ACE. Therefore, a Telnet/SSH session or ping reply is allowed from a device on the 192.168.10.0/24 network.
- What is the function of the pass action on a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall?
- logging of rejected or dropped packets
- inspecting traffic between zones for traffic control
- tracking the state of connections between zones
- orwarding traffic from one zone to another*
The pass action performed by Cisco IOS ZPF permits forwarding of traffic in a manner similar to the permit statement in an access control list.
- When a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall is being configured via CLI, which step must be taken after zones have been created?
- Assign interfaces to zones.
- Establish policies between zones.*
- Identify subsets within zones.
- Design the physical infrastructure.
The steps for configuring zones in a Zone-Based Policy Firewall are as follows:
Step 1. Determine the zones.
Step 2. Establish policies between zones.
Step 3. Design the physical infrastructure.
Step 4. Identify subsets within zones and merge traffic requirements.
- A network administrator is implementing a Classic Firewall and a Zone-Based Firewall concurrently on a router. Which statement best describes this implementation?
- An interface must be assigned to a security zone before IP inspection can occur.
- Both models must be implemented on all interfaces.
- The two models cannot be implemented on a single interface.*
- A Classic Firewall and Zone-Based Firewall cannot be used concurrently.
Both a Classic Firewall and Zone-Based Firewall can be implemented concurrently on a router, but they cannot both be configured on a single interface.
- Which two rules about interfaces are valid when implementing a Zone-Based Policy Firewall? (Choose two.)
- If one interface is a zone member, but the other is not, all traffic will be passed.
- If neither interface is a zone member, then the action is to pass traffic.*
- If both interfaces are members of the same zone, all traffic will be passed.*
- If one interface is a zone member and a zone-pair exists, all traffic will be passed.
- If both interfaces belong to the same zone-pair and a policy exists, all traffic will be passed.
The rules for traffic transiting through the router are as follows:
If neither interface is a zone member, then the resulting action is to pass the traffic.
If both interfaces are members of the same zone, then the resulting action is to pass the traffic.
If one interface is a zone member, but the other is not, then the resulting action is to drop the traffic regardless of whether a zone-pair exists.
If both interfaces belong to the same zone-pair and a policy exists, then the resulting action is inspect, allow, or drop as defined by the policy.
- Which command will verify a Zone-Based Policy Firewall configuration?
- show interfaces
- show zones
- show running-config*
- show protocols
The ZPF configuration can be verified with the show running-config, show policy-map, show class-map, show zone security, and show zone-pair security commands.
- Refer to the exhibit. The network “A” contains multiple corporate servers that are accessed by hosts from the Internet for information about the corporation. What term is used to describe the network marked as “A”?
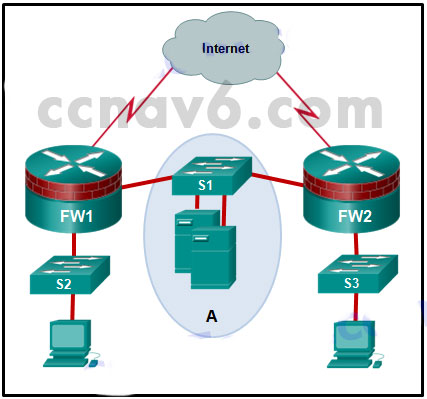
- internal network
- untrusted network
- perimeter security boundary
- DMZ*
A demilitarized zone or DMZ is a network area protected by one or more firewalls. The DMZ typically contains servers that are commonly accessed by external users. A web server is commonly contained in a DMZ.
- Which type of packet is unable to be filtered by an outbound ACL?
- multicast packet
- ICMP packet
- broadcast packet
- router-generated packet*
Traffic that originates within a router such as pings from a command prompt, remote access from a router to another device, or routing updates are not affected by outbound access lists. The traffic must flow through the router in order for the router to apply the ACEs.
- When a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall is being configured, which two actions can be applied to a traffic class? (Choose two.)
- drop*
- log
- forward
- hold
- inspect*
- copy
The three actions that can be applied are inspect, drop,and pass.
Inspect – This action offers state-based traffic control.
Drop – This is the default action for all traffic. Similar to the implicit deny any at the end of every ACL, there is an explicit drop applied by the IOS to the end of every policy map.
Pass – This action allows the router to forward traffic from one zone to another.
- Fill in the blank.
A stateful firewall monitors the state of connections as network traffic flows into and out of the organization.
- Fill in the blank.
The pass action in a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall is similar to a permit statement in an ACL.










