9.3.8 Lab – Exploring Nmap (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology

Objectives
- Part 1: Exploring Nmap
- Part 2: Scanning for Open Ports
Background / Scenario
Port scanning is usually part of a reconnaissance attack. There are a variety of port scanning methods that can be used. We will explore how to use the Nmap utility. Nmap is a powerful network utility that is used for network discovery and security auditing.
Required Resources
- CyberOps Workstation virtual machine
- Internet access
Instructions
Part 1: Exploring Nmap
In this part, you will use manual pages (or man pages for short) to learn more about Nmap.
The man [ program |utility | function] command displays the manual pages associated with the arguments. The manual pages are the reference manuals found on Unix and Linux OSs. These pages can include these sections: Name, Synopsis, Descriptions, Examples, and See Also.
a. Start CyberOps Workstation VM.
b. Open a terminal.
c. At the terminal prompt, enter man nmap.
[analyst@secOps ~]$ man nmap
What is Nmap?
What is nmap used for?
d. While in the man page, you can use the up and down arrow keys to scroll through the pages. You can also press the space bar to forward one page at a time.
To search for a specific term or phrase use enter a forward slash (/) or question mark (?) followed by the term or phrase. The forward slash searches forward through the document, and the question mark searches backward through the document. The key n moves to the next match.
Type /example and press ENTER. This will search for the word example forward through the man page.
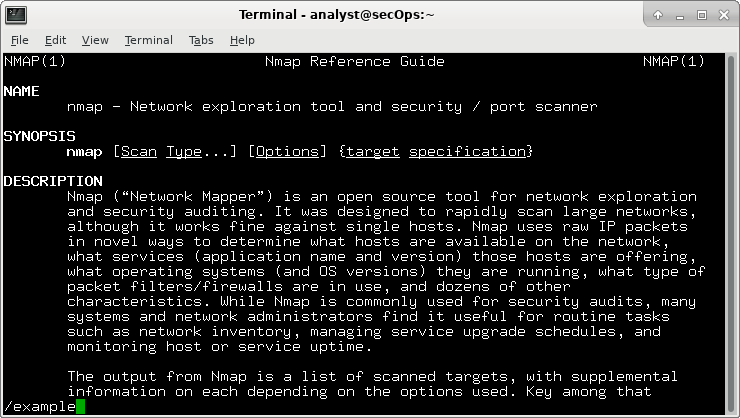
e. In the first instance of example, you see three matches. To move to the next match, press n.
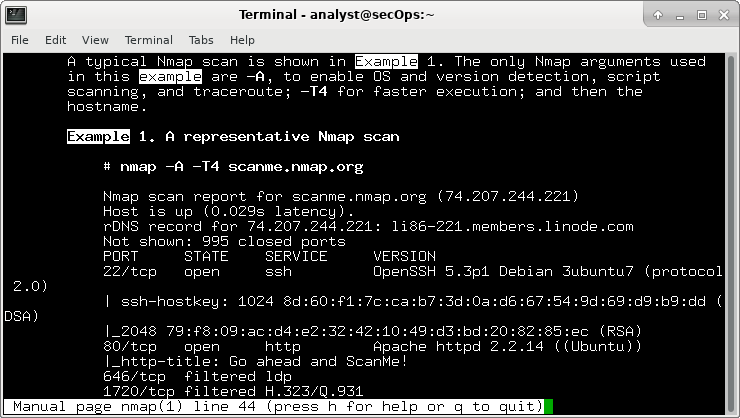
Look at Example 1.
What is the nmap command used?
Use the search function to answer the following questions.
What does the switch -A do?
What does the switch -T4 do?
f. Scroll through the page to learn more about nmap. Type q when finished.
Part 2: Scanning for Open Ports
In this part, you will use the switches from the example in the Nmap man pages to scan your localhost, your local network, and a remote server at scanme.nmap.org.
Step 1: Scan your localhost.
a. If necessary, open a terminal on the VM. At the prompt, enter nmap -A -T4 localhost. Depending on your local network and devices, the scan will take anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes.
[analyst@secOps ~]$ nmap -A -T4 localhost Starting Nmap 7.40 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-05-01 17:20 EDT Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1) Host is up (0.000056s latency). Other addresses for localhost (not scanned): ::1 rDNS record for 127.0.0.1: localhost.localdomain Not shown: 996 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.0.8 or later | ftp-anon: Anonymous FTP login allowed (FTP code 230) |_-rw-r--r-- 1 0 0 0 Apr 19 15:23 ftp_test <some output omitted>
b. Review the results and answer the following questions.
Which ports and services are opened?
For each of the open ports, record the software that is providing the services.
Step 2: Scan your network.
Warning: Before using Nmap on any network, please gain the permission of the network owners before proceeding.
a. At the terminal command prompt, enter ip address to determine the IP address and subnet mask for this host. For this example, the IP address for this VM is 10.0.2.15 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
[analyst@secOps ~]$ ip address
<output omitted>
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:ed:af:2c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.0.2.15/24 brd 10.0.2.255 scope global dynamic enp0s3
valid_lft 85777sec preferred_lft 85777sec
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:feed:af2c/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Record the IP address and subnet mask for your VM.
Which network does your VM belong to?
b. To locate other hosts on this LAN, enter nmap -A -T4 network address/prefix. The last octet of the IP address should be replaced with a zero. For example, in the IP address 10.0.2.15, the .15 is the last octet. Therefore, the network address is 10.0.2.0. The /24 is called the prefix and is a shorthand for the netmask 255.255.255.0. If your VM has a different netmask, search the internet for a “CIDR conversion table” to find your prefix. For example, 255.255.0.0 would be /16. The network address 10.0.2.0/24 is used in this example
Note: This operation can take some time, especially if you have many devices attached to the network. In one test environment, the scan took about 4 minutes.
[analyst@secOps ~]$ nmap -A -T4 10.0.2.0/24 Starting Nmap 7.40 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-05-01 17:13 EDT <output omitted> Nmap scan report for 10.0.2.15 Host is up (0.00019s latency). Not shown: 997 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 21/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.0.8 or later | ftp-anon: Anonymous FTP login allowed (FTP code 230) |_-rw-r--r-- 1 0 0 0 Mar 26 2018 ftp_test | ftp-syst: | STAT: | FTP server status: | Connected to 10.0.2.15 | Logged in as ftp | TYPE: ASCII | No session bandwidth limit | Session timeout in seconds is 300 | Control connection is plain text | Data connections will be plain text | At session startup, client count was 1 | vsFTPd 3.0.3 - secure, fast, stable |_End of status 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2 (protocol 2.0) 23/tcp open telnet Openwall GNU/*/Linux telnetd Service Info: Host: Welcome; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel Post-scan script results: | clock-skew: | 0s: | 10.0.2.4 | 10.0.2.3 |_ 10.0.2.2 Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (4 hosts up) scanned in 346.89 seconds
How many hosts are up?
From your Nmap results, list the IP addresses of the hosts that are on the same LAN as your VM. List some of the services that are available on the detected hosts.
Step 3: Scan a remote server.
a. Open a web browser and navigate to scanme.nmap.org. Please read the message posted.
What is the purpose of this site?
b. At the terminal prompt, enter nmap -A -T4 scanme.nmap.org.
[analyst@secOps Desktop]$ nmap -A -T4 scanme.nmap.org Starting Nmap 7.40 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-05-01 16:46 EDT Nmap scan report for scanme.nmap.org (45.33.32.156) Host is up (0.040s latency). Other addresses for scanme.nmap.org (not scanned): 2600:3c01::f03c:91ff:fe18:bb2f Not shown: 992 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 6.6.1p1 Ubuntu 2ubuntu2.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0) | ssh-hostkey: | 1024 ac:00:a0:1a:82:ff:cc:55:99:dc:67:2b:34:97:6b:75 (DSA) | 2048 20:3d:2d:44:62:2a:b0:5a:9d:b5:b3:05:14:c2:a6:b2 (RSA) |_ 256 96:02:bb:5e:57:54:1c:4e:45:2f:56:4c:4a:24:b2:57 (ECDSA) 25/tcp filtered smtp 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.7 ((Ubuntu)) |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.7 (Ubuntu) |_http-title: Go ahead and ScanMe! 135/tcp filtered msrpc 139/tcp filtered netbios-ssn 445/tcp filtered microsoft-ds 593/tcp filtered http-rpc-epmap 4444/tcp filtered krb524 9929/tcp open nping-echo Nping echo 31337/tcp open tcpwrapped Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 23.96 seconds
c. Review the results and answer the following questions.
Which ports and services are opened?
Which ports and services are filtered?
What is the IP address of the server?
What is the operating system?
Reflection Question
Nmap is a powerful tool for network exploration and management. How can Nmap help with network security? How can Nmap be used by a threat actor as a nefarious tool?