CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – Routing Essentials and EIGRP Exam Answers
Chapters 6 – 7: Routing Essentials and EIGRP Exam Answers
1. Which type of routing protocol uses LSAs and TLVs to support extended features?
- distance vector
- link-state
- path vector
- hybrid
2. What are two characteristics of link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
- They periodically send full routing table updates to directly connected neighbors.
- They use path attributes to determine the best loop-free path.
- They can load balance across unequal metric cost paths.
- They use more CPU and memory resources than distance vector protocols do.
- They provide routers with a synchronized identical map of the network.
3. What data is used by OSPF and ISIS for loop prevention?
- a synchronized map of the network
- hop count to the destination
- feasible distance calculation to the destination
- autonomous system path to the destination
4. Which routing protocol incorporates characteristics of both distance vector and link-state protocols?
- EBGP
- EIGRP
- ISIS
- iBGP
5. How do EIGRP routers establish and maintain neighbor relationships?
- by comparing known routes to information received in updates
- by dynamically learning new routes from neighbors
- by exchanging hello packets with neighboring routers
- by exchanging routing tables with directly attached routers
- by exchanging neighbor tables with directly attached routers
6. A router has installed several routes into the routing table. How will the router determine which route to use to forward packets?
- the longest prefix match
- the highest metric
- the lowest metric
- the lowest administrative distance
7. What is the effect of configuring the ipv6 unicast-routing command on a router?
- to prevent the router from joining the all-routers multicast group
- to assign the router to the all-nodes multicast group
- to permit only unicast packets on the router
- to enable the router as an IPv6 router
8. Why would a floating static route be configured with an administrative distance that is higher than the administrative distance of a dynamic routing protocol that is running on the same router?
- to be used as a backup route
- to be the priority route in the routing table
- to load-balance the traffic
- to act as a gateway of last resort
9. Which static route statement shows a recursive IPv6 static route?
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/56 S0/0/0
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/56 2001:db8:1000:10::1
- ipv6 route 0::/0 S0/0/0
- ipv6 route 2001:db8:cafe:1::/56 S0/0/0 2001:db8:1000:10::1
- ipv6 route 0::/0 S0/0/0 254
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which command will properly configure an IPv6 static route on R2 that will allow traffic from PC2 to reach PC1 without any recursive lookups by router R2?

- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 2001:db8:32::1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:32::1
- R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:10:12::/64 S0/0/0
11. Refer to the exhibit. Router R1 has an OSPF neighbor relationship with the ISP router over the 192.168.0.32 network. The 192.168.0.36 network link should serve as a backup when the OSPF link goes down. The floating static route command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/1 100 was issued on R1 and now traffic is using the backup link even when the OSPF link is up and functioning. Which change should be made to the static route command so that traffic will only use the OSPF link when it is up?
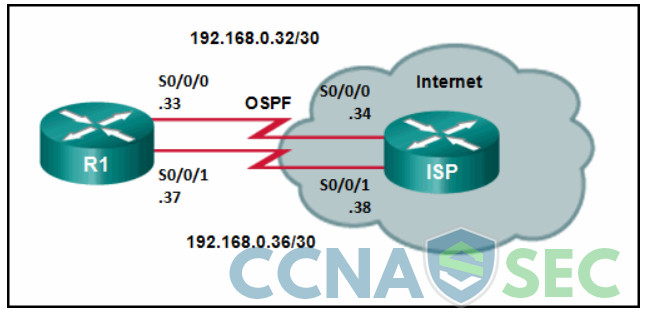
- Add the next hop neighbor address of 192.168.0.36.
- Change the administrative distance to 1.
- Change the destination network to 192.168.0.34.
- Change the administrative distance to 120.
12. What is used by BGP to guarantee a loop free path to reach a destination?
- the count of router hops to reach a destination
- a record of each autonomous system that a routing advertisement has traversed
- a distance calculation based on cumulative delay and minimum bandwidth
- the cumulative cost as measured in bandwidth
13. What is the purpose for creating VRFs on a router?
- to determine the vector to reach a destination network
- to keep a record of all autonomous systems that routing advertisements have traversed
- to isolate paths
- to prevent routing loops
14. Which technology creates segmentation between network interfaces, IP addresses, and routing tables?
- virtual routing and forwarding
- multiprotocol label switching
- virtual router redundancy protocol
- virtual LANs
15. What is the administrative distance of an IS-IS route?
- 110
- 170
- 90
- 115
16. Refer to the exhibit. R2 has two possible paths to the 192.168.10.4 network. What would make the alternate route meet the feasibility condition?
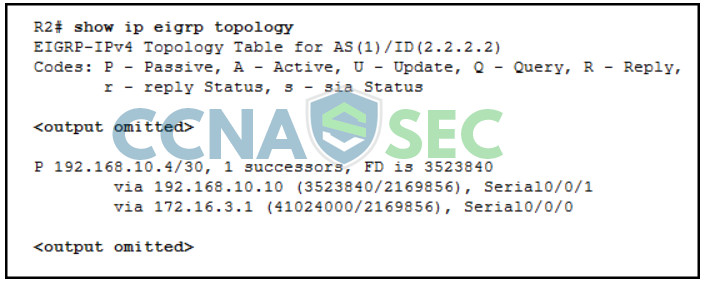
- a reported distance greater than 41024000
- a feasible distance greater than 41024000
- an administrative distance less than 170
- a reported distance less than 3523840
17. Which protocol number is used to indicate that an EIGRP packet is encapsulated in an IP packet?
- 6
- 17
- 88
- 89
18. Match the description to the EIGRP packet type. (Not all options are used.)
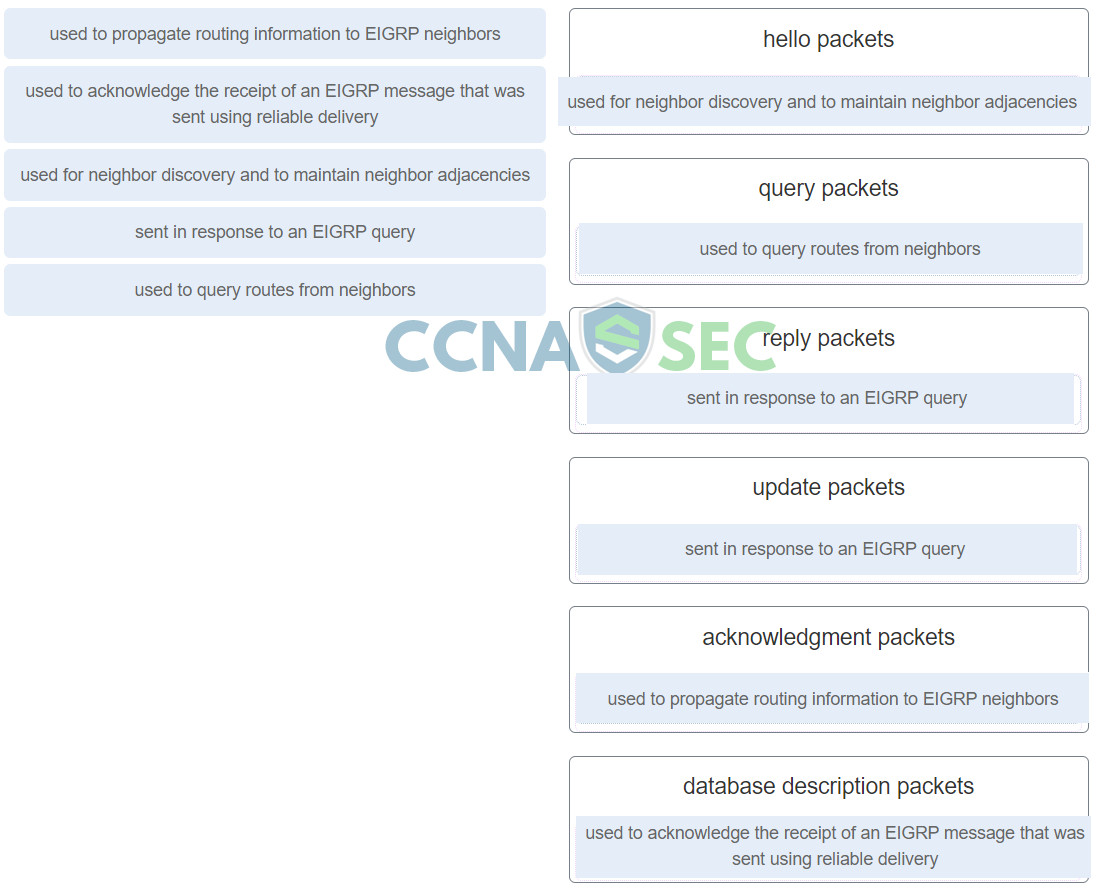
- Hello packets – Used for neighbor discovery and to maintain neighbor adjacencies.
- Update packets – Used to propagate routing information to EIGRP neighbors.
- Acknowledgment packets – Used to acknowledge the receipt of an EIGRP message that was sent using reliable delivery.
- Query packets – Used to query routes from neighbors.
- Reply packets – Sent in response to an EIGRP query.
19. Which statement describes the autonomous system number used in EIGRP configuration on a Cisco router?
- It is a globally unique autonomous system number that is assigned by IANA.
- It identifies the ISP that provides the connection to network of the organization.
- It carries the geographical information of the organization.
- It functions as a process ID in the operation of the router.
20. Which bandwidth value is used when calculating the EIGRP metric of a route?
- the slowest bandwidth of all interfaces on the router
- the slowest bandwidth of all outgoing interfaces between the source and destination
- the fastest bandwidth of all interfaces on the router
- the fastest bandwidth of all outgoing interfaces between the source and destination
21. Refer to the exhibit. All the routers that are displayed are part of the EIGRP domain. Assuming EIGRP metric weights are not altered in the configurations, which path will a packet take that originates from a host on the 192.168.1.0/24 network and is going to a host on the 192.168.2.0/24 network?
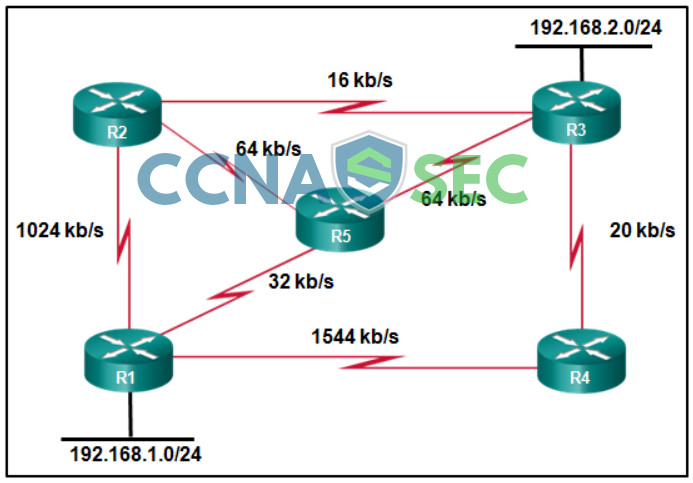
- R1, R2, R3
- R1, R5, R3
- R1, R4, R3
- R1, R2, R5, R3
22. Which two metric weights are set to one by default when costs in EIGRP are being calculated? (Choose two.)
- k2
- k5
- k3
- k1
- k6
- k4
23. Which routing protocol supports load balancing across links with unequal costs?
- OSPFv3
- RIPv2
- EIGRP
- OSPFv2
24. How has the EIGRP routing protocol improved by having interface delay measured in picoseconds instead of microseconds?
- It provides better metrics for high speed interfaces.
- It improves performance and communication time between directly connected neighbor routers.
- It allows for a larger number of networks.
- It speeds up convergence.
25. If all router Ethernet interfaces in an EIGRP network are configured with the default EIGRP timers, how long will a router wait by default to receive an EIGRP packet from its neighbor before declaring the neighbor unreachable?
- 10 seconds
- 15 seconds
- 20 seconds
- 30 seconds
26. What two conditions will result in an EIGRP route going into the active state? (Choose two.)
- One neighbor has not met the feasibility condition.
- The network has been recalculated.
- The successor is down.
- There is no feasible successor.
- The router is not sending queries.
27. An EIGRP router loses the route to a network. Its topology table contains two feasible successors to the same network. What action will the router take?
- The router uses the default route.
- The best alternative backup route is immediately inserted into the routing table.
- The router will query neighbors for an alternate route.
- The DUAL algorithm is recomputed to find an alternate route.
28. Which feature of the EIGRP routing protocol can provide fast re-convergence without DUAL recomputation in the event of a route failure?
- having a route in the passive state
- having a feasible successor route
- having a route in the active state
- having a successor route
29. What are two benefits of applying summarization to networks within a company that uses the EIGRP routing protocol? (Choose two.)
- reduced number of Layer 3 switches required
- reduced size of routing tables
- reduced impact when a route goes active
- reduced number of hops the packet must travel throughout the network
- reduced number of routers that must maintain a neighbor adjacency
30. Refer to a portion of an EIGRP topology table:
P 172.18.3.0/24, 1 successors, __ is 2172416 via 172.18.4.3 (2172416/28160), Serial0/0/1 P 172.18.5.0/24, 1 successors, __ is 2495120 via 172.18.6.3 (2495120/227692), Serial0/1/0 P 192.168.24.0/24, 1 successors, __ is 2684416 via 192.168.13.5 (2684416/2072316), Serial0/0/0 via 172.18.4.3 (2854912/2342912), Serial0/0/1 P 10.34.1.0/24, 1 successors, __ is 3072 via 10.13.1.3 (3072/2937), GigabitEthernet0/1 via 10.14.1.4 (5376/2937), GigabitEthernet0/2
What is the feasible distance of the 172.18.5.0/24 route?
- 2854912
- 227692
- 2342912
- 2495120