CCNPv8 ENCOR ( Version 8.0) – L2 Redundancy Exam Answers
CCNPv8 ENCOR (Version 8.0) – L2 Redundancy Exam Answers
Chapters 1 – 5: L2 Redundancy Exam Answers
1. What is the goal of Layer 3 switching?
- to process packets at Layer 2 switching speeds while utilizing the scalability of routing
- to provide a better path to the Internet without using routing protocols
- to integrate all of the networking functions into one device
- to implement the routing process by using routed protocols
2. Which two statements are true about routed ports on a multilayer switch? (Choose two.)
- To create a routed port requires removal of Layer 2 port functionality with the no switchport interface configuration command.
- The interface vlan global configuration command is used to create a routed port.
- A routed port is not associated with a particular VLAN.
- A routed port behaves like a regular router interface and supports VLAN subinterfaces.
- A routed port is a physical switch port with Layer 2 capability.
3. Which two statements are true about the 802.1Q trunking protocol? (Choose two.)
- The native VLAN interface configurations must match at both ends of the link or frames could be dropped.
- Untagged frames will be placed in the configured native VLAN of a port.
- It is a proprietary protocol that is supported on Cisco switches only.
- Private VLAN configurations are not supported.
4. Which technology does CEF switching use on Cisco hardware-based routers to forward packets?
- forwarding engines implemented in specialized ASICs
- interVLAN routing using subinterfaces
- router general-purpose CPU
- route processors using stateful switchover
5. What type of specialized memory is used to facilitate high performance switching in Cisco multilayer switches?
- address resolution protocol (ARP) memory
- content-addressable memory (CAM)
- ternary content addressable memory (TCAM)
- Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) memory
6. Which protocol is required for Cisco Express Forwarding to be able to successfully forward packets on a multilayer switch?
- VLAN Trunking Protocol
- Cisco Discovery Protocol
- Dynamic Trunking Protocol
- Spanning Tree Protocol
- Address Resolution Protocol
7. If left to default configuration settings, what will determine which switch becomes the spanning-tree root bridge in a Layer 2 domain?
- the lowest switch MAC address
- the highest bridge ID
- the highest bridge priority
- the highest management IP address
8. During the implementation of Spanning Tree Protocol, all switches are rebooted by the network administrator. What is the first step of the spanning-tree election process?
- All the switches send out BPDUs advertising themselves as the root bridge.
- Each switch with a lower root ID than its neighbor will not send BPDUs.
- Each switch determines the best path to forward traffic.
- Each switch determines what port to block to prevent a loop from occurring.
9. After the election of the root bridge has been completed, how will switches find the best paths to the root bridge?
- Each switch will analyze the port states of all neighbors and use the designated ports to forward traffic to the root.
- Each switch will analyze the sum of the hops to reach the root and use the path with the fewest hops.
- Each switch will analyze the sum of all port costs to reach the root and use the path with the lowest cost.
- Each switch will analyze the BID of all neighbors to reach the root and use the path through the lowest BID neighbors.
10. Which statement is true about the port roles of the 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol?
- An alternate or backup port can immediately change to a forwarding state without waiting for the network to converge.
- Cisco-proprietary enhancements to the legacy 802.1D, such as UplinkFast and BackboneFast, are compatible with RSTP.
- Ports are manually configured to be in the designated role.
- It takes an edge port 15 seconds to go from blocking to forwarding.
11. Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
- cost
- MAC address
- extended system ID
- IP address
- bridge priority
- port ID
12. In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network? (Choose two.)
- forwarding
- listening
- blocking
- learning
- disabled
13. Which STP priority configuration would ensure that a switch would always be the root switch?
- spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 61440
- spanning-tree vlan 10 root primary
- spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 0
- spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 4096
14. Why is it important that the network administrator consider the spanning-tree network diameter when choosing the root bridge?
- The cabling distance between the switches is 100 meters.
- BPDUs may be discarded because of expiring timers.
- The network diameter limitation is 9.
- Convergence is slower as the BPDU travels away from the root.
15. A network administrator enters the spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default command. What is the result of this command being issued on a Cisco switch?
- Any switch port that has been configured with PortFast will be error-disabled if it receives a BPDU.
- Any trunk ports will be allowed to connect to the network immediately, rather than waiting to converge.
- Any switch port will be error-disabled if it receives a BPDU.
- Any switch port that receives a BPDU will ignore the BPDU message.
16. In what situation would a network administrator most likely implement root guard?
- on all switch ports that connect to a Layer 3 device
- on all switch ports that connect to another switch that is not the root bridge
- on all switch ports that connect to host devices
- on all switch ports that connect to another switch
- on all switch ports (used or unused)
17. Which technology is used to protect the switched infrastructure from problems caused by receiving BPDUs on ports that should not be receiving them?
- Loop guard
- PortFast
- BPDU guard
- RSPAN
- Root guard
18. What are the two options that describe the effects of the spanning-tree portfast command? (Choose two.)
- Enabling PortFast on trunks that connect to other switches improves convergence.
- If a switch port is configured with PortFast, it is an access port that immediately transitions from a blocking to forwarding state.
- If the switch port is configured with PortFast, it waits 15 seconds before transitioning from a blocking to forwarding state.
- Portfast bypasses the learning state and moves immediately into blocking.
- Portfast enables the port to bypass the listening and learning states of STP.
19. Which statement describes the term blocking in the operation of STP?
- It indicates that the port has transitioned from a blocking state and can send or receive BPDUs, but cannot forward any other network traffic.
- It indicates that the port is in an administratively off position.
- It is a port state that is enabled but does not forward any traffic to ensure that a loop does not occur.
- It is a port state that work traffic that it receives, but only forwards BPDUs and not any other network traffic.
20. What are two configuration parameters that must match for all switches in the same MST region? (Choose two.)
- region name
- trunk link encapsulation method
- port status
- version number
- bridge priority
21. Assuming that all switches in a network have the default bridge priority for each MST instance, what effect does the command spanning-tree mst 10 root seconday have when entered on a single switch?
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 28672 for MST instance 10
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 24586 for MST instance 10
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 24576 for MST instance 10
- sets the bridge priority on the switch to 24582 for MST instance 10
spanning-tree mst instance-number priority priority , where the priority is a value between 0 and 61,440, in increments of 4096
spanning-tree mst instance-number root { primary | secondary }[ diameter diameter ], where the primary keyword sets the priority to 24,576, and the secondary keyword sets the priority to 28,672
22. Which two statements describe the MST internal spanning tree instance? (Choose two)
- It is always instance 0.
- It carries all VLANs traffic.
- It runs on all switch port interfaces of switches that are designated as root bridges.
- It runs on all switch port interfaces of switches in the MST region.
- It carries identical setup information among interconnected MST regions.
23. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring MST tuning on SW1. The objective is to change the path cost value of the interface Gi1/0/1 to represent a higher-speed bandwidth link. Which value could be used in the command spanning-tree mst 0 cost for this task?
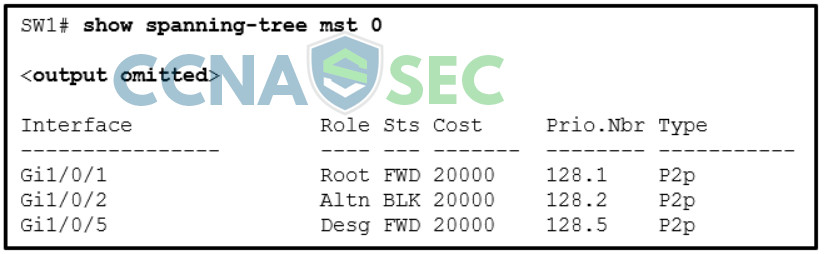
- 0
- 1
- 24576
- 32768
24. What are two misconfigurations within an MST region that might introduce port blocking unintentionally? (Choose two.)
- misconfigured region name across the MST region
- trunk link pruning
- too many VLANs assigned to an instance
- VLAN assignment to the IST
- misconfigured revision number across the MST region
25. How does an MST region send VLAN information through the PVST simulation mechanism to a switch that runs PVST+?
- It sends out one PVST+ BPDU that maps all VLANs into VLAN1.
- It sends out multiple PVST+ BPDUs, one for each VLAN, plus the IST.
- It sends out PVST+ BPDUs, one for each VLAN, using the information from the IST.
- It sends out one PVST+ BPDU with the information from the IST.
26. The network administrator wants to configure a switch to pass VLAN update information to other switches in the domain but not update its own local VLAN database. Which two steps should the administrator perform to achieve this? (Choose two.)
- Configure VTP version 1 on the switch.
- Configure the switch with the same VTP domain name as other switches in the network.
- Verify that the switch has a higher configuration revision number.
- Configure the VTP mode of the switch to transparent.
- Reset the VTP counters.
27. Which Cisco proprietary protocol is used for dynamically forming a trunk connection between two switches?
- VTP
- PAgP
- STP
- DTP
28. Which LACP technology can identify and remove a LACP enabled link from an EtherChannel within three seconds when the link is experiencing connectivity issues?
- LACP min-links
- LACP port priority
- LACP system priority
- LACP fast
LACP port priority allows an LACP enabled switch to select which member interfaces are active within a port-channel that has more member interfaces than the maximum allowed.
LACP system priority allows an LACP enabled switch to be designated as the master switch for a port-channel.
LACP min-links is used to configure a required minimum number of physical connections that must be active in order for the EtherChannel to stay active.
29. Which LACP technology is used for designating a specific number of member interfaces that must remain active in order for the EtherChannel bundle to be usable?
- LACP port priority
- LACP system priority
- LACP min-links
- LACP fast
LACP port priority allows an LACP enabled switch to select which member interfaces are active within a port-channel that has more member interfaces than the maximum allowed.
LACP system priority allows an LACP enabled switch to be designated as the master switch for a port-channel.
LACP min-links is used to configure a required minimum number of physical connections that must be active in order for the EtherChannel to stay active.
30. Which LACP technology is used for designating which member interfaces will be active in a port-channel configuration where there are more member interfaces than the maximum allowed?
- LACP system priority
- LACP fast
- LACP port priority
- LACP min-links
LACP port priority allows an LACP enabled switch to select which member interfaces are active within a port-channel that has more member interfaces than the maximum allowed.
LACP system priority allows an LACP enabled switch to be designated as the master switch for a port-channel.
LACP min-links feature is used to configure a required minimum number of physical connections that must be active in order for the EtherChannel to stay active.
31. Refer to the exhibit. The administrator tried to create an EtherChannel between S1 and the other two switches via the commands that are shown, but was unsuccessful. What is the problem?
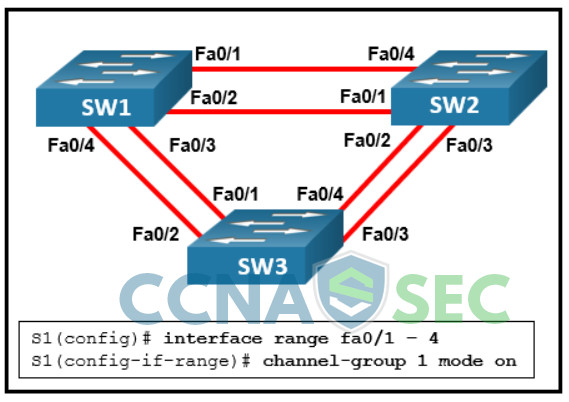
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Layer 3 switches.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches through the same EtherChannel link.
- Traffic cannot be sent to two different switches, but only to two different devices like an EtherChannel-enabled server and a switch.
- Traffic can only be sent to two different switches if EtherChannel is implemented on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
